For Journal Club on August 6, Nate Krefman presented the following paper:
Centromere-like regions in the budding yeast genome. Lefrançois P, Auerbach RK, Yellman CM, Roeder GS, Snyder M. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003209. PMID: 23349633.
For Journal Club on August 6, Nate Krefman presented the following paper:
Centromere-like regions in the budding yeast genome. Lefrançois P, Auerbach RK, Yellman CM, Roeder GS, Snyder M. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003209. PMID: 23349633.
For Journal Club on August 6, Eric Lewellyn presented the following paper:
Actin filament severing by cofilin dismantles actin patches and produces mother filaments for new patches. Chen Q, Pollard TD. Curr Biol. 2013 Jul 8;23(13):1154-62. PMID: 23727096.
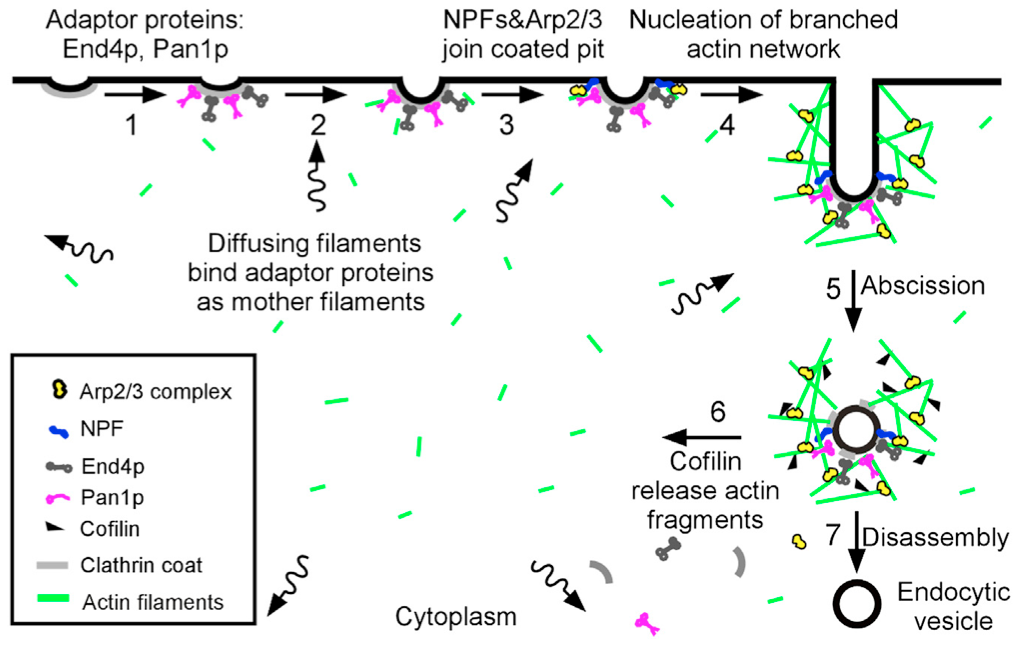
“Sever, diffuse and trigger” model for actin filament turnover in actin patches. The 7 steps (numbers next to the arrows) are (1) clathrin coated pits bind adaptor proteins End4p and Pan1p, (2) short, diffusing actin filaments bind to End4p and Pan1p associated with coated pits, and (3) Arp2/3 complex interacts with these mother filaments and nucleation promoting factors to (4) initiate branching nucleation of actin filaments that promote elongation of the endocytic tubule. (5) After abscission of the vesicle, (6) cofilin severs actin filaments to generate a pool of short, diffusing actin filaments, some of which return to the cycle at step 2.
For Journal Club on July 22, Connie Peng presented the following paper:
Mps1 and Ipl1/Aurora B act sequentially to correctly orient chromosomes on the meiotic spindle of budding yeast. Meyer RE, Kim S, Obeso D, Straight PD, Winey M, Dawson DS. Science. 2013 Mar 1;339(6123):1071-4. PMID: 23371552
For Microtubules and Mitosis Journal Club on April 25, members of the Drubin/Barnes Lab, Eva Nogales Lab, and Ahmet Yildiz Lab will discuss the following paper, selected by Stu Howes:
Synergy between XMAP215 and EB1 increases microtubule growth rates to physiological levels. Zanic M, Widlund PO, Hyman AA, Howard J. Nat Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;15(6):688-93. PMID: 23666085.
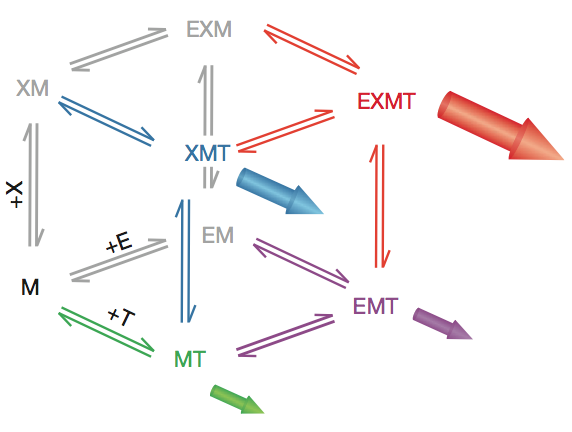
Reaction scheme for an enzymatic reaction with two non-essential activators. The microtubule end is viewed as an enzyme that catalyses the reaction: tubulin in solution (substrate)→tubulin in the polymer (product) by providing a much more efficient pathway than direct incorporation into the lattice. XMAP215 and EB1 are viewed as two non-essential enzyme activators that accelerate the net rate of addition at the end. Filled arrows represent the flux of polymerization through a particular vertex. M, microtubule end; T, free tubulin; X, XMAP215; E, EB1.
For our Journal Club on June 17, Jessica Marks will present the following paper:
Amphipathic antenna of an inward rectifier K+ channel responds to changes in the inner membrane leaflet. Iwamoto M, Oiki S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 8;110(2):749-54. PMID: 23267068.
For Microtubules and Mitosis Journal Club on April 25, members of the Drubin/Barnes Lab, Eva Nogales Lab, and Ahmet Yildiz Lab discussed the following paper, selected by Anthony Cormier:
Tension sensing by Aurora B kinase is independent of survivin-based centromere localization. Campbell CS, Desai A. Nature. 2013 May 2;497(7447):118-21. PMID: 23604256.
For our Journal Club on April 29, Sun Hae Hong presented the following paper:
The molecular basis for the endocytosis of small R-SNAREs by the clathrin adaptor CALM. Miller SE, Sahlender DA, Graham SC, Höning S, Robinson MS, Peden AA, Owen DJ. Cell. 2011 Nov 23;147(5):1118-31. PMID: 22118466
For our new Microtubules and Mitosis Journal Club on April 25, members of the Drubin/Barnes Lab, Eva Nogales Lab, and Ahmet Yildiz Lab discussed the following paper, selected by Nate Krefman:
Estimating the microtubule GTP cap size in vivo. Seetapun D, Castle BT, McIntyre AJ, Tran PT, Odde DJ. Curr Biol. 2012 Sep 25;22(18):1681-7. PMID: 22902755